What Is The Tissue Makeup Of A Fibroid Tumor
Slideshow: A Visual Guide to Uterine Fibroids
Medically Reviewed by Nivin Todd, MD on May 31, 2020
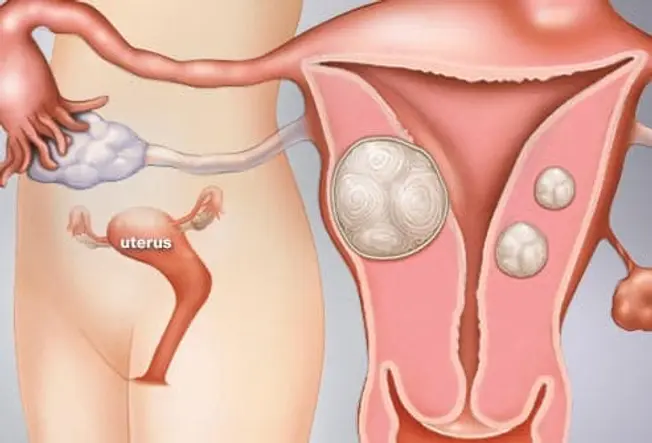
What Are Uterine Fibroids?
1/19
Uterine fibroids are noncancerous growths of the musculus tissue of the uterus. Fibroids can range in number and size from a single growth to multiple growths, and from very small to big. As many as seventy% to 80% of all women will have fibroids by age 50. The medical term for fibroids is leiomyoma or myoma.
Symptoms of Fibroids: Force per unit area
two/19
Fibroids may cause very mild symptoms, none at all or symptoms tin can exist severe. In women who practice experience symptoms, these uterine growths tin can cause:
- Pressure level on the bladder or rectum
- Frequent urination
- Constipation and/or rectal pain
- Lower back and/or abdominal pain
If fibroids become very large, they tin distend the tummy, making a woman expect pregnant.

Symptoms of Fibroids: Period Changes
3/19
Fibroids may besides cause changes to a woman'southward menstruum, including:
- Mild to severe cramping and pain
- Heavier haemorrhage, sometimes with blood clots
- Longer or more frequent menses
- Spotting or bleeding between periods
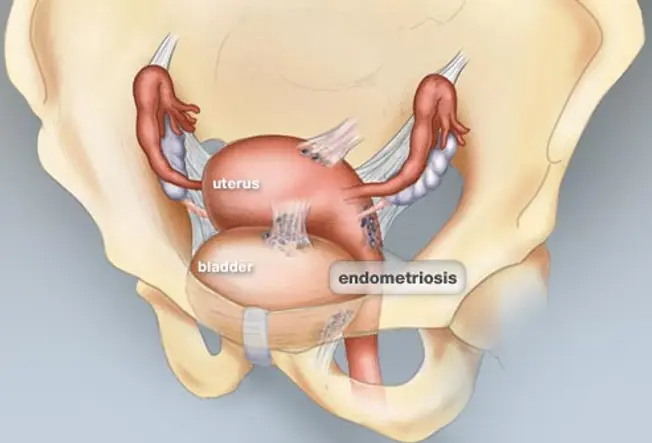
Fibroids or Endometriosis?
iv/19
Fibroids are one crusade of severe menstrual pain, but the pain also can exist caused by endometriosis. Endometriosis occurs when tissue from the inner lining of the uterus grows in other parts of the torso -- illustrated hither by growths on the outside of the uterus and bladder. This tissue breaks down and bleeds during your period, causing pain during your cycle and painful scar tissue. The hurting of fibroids or endometriosis as well can occur betwixt periods.
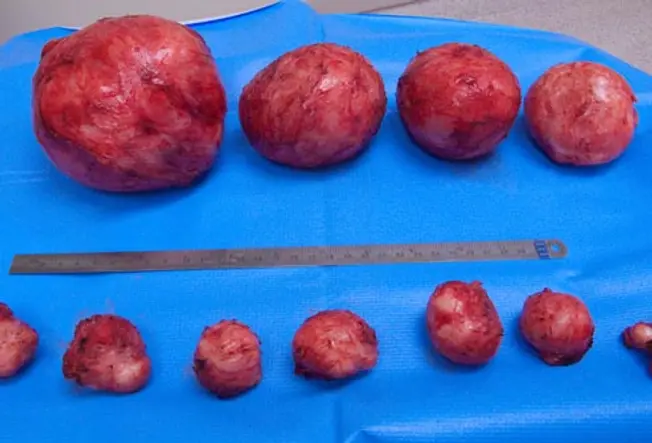
What Causes Fibroids?
5/19
The exact cause of fibroids is unknown. Their growth has been linked to the female hormones estrogen and progesterone. Studies take constitute that women who start their periods at a younger age are more likely to develop fibroids. Although taking female hormones is linked to fibroids, the use of nascency control pills is not.
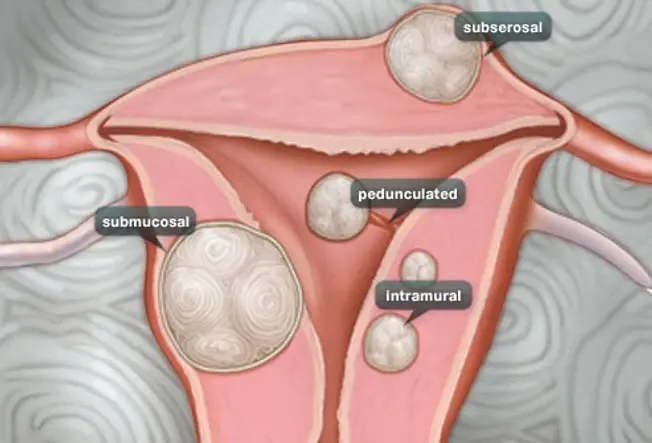
Types of Fibroids
6/19
- Intramural fibroids, the well-nigh common, abound in the wall of the uterus.
- Subserosal fibroids abound on the outside of the uterus. Equally they abound larger, they tin cause pain due to their size or pressure put on nearby organs.
- Submucosal fibroids grow merely underneath the uterine lining and can oversupply into the uterus cavity and lead to heavy bleeding and other more serious complications.
- Pedunculated fibroids abound on modest stalks within or outside the uterus.
It'southward possible to accept more than one blazon of fibroid.

Who Gets Fibroids?
7/xix
While it's unclear why women develop fibroids, some patterns take been observed.
- They commonly occur betwixt the ages of 30 and forty.
- They are more common in blackness women.
- They grow more chop-chop and appear at a younger age in black women.
- Having a family unit member with fibroids increases a woman'southward run a risk.
- Beingness overweight or obese and having high blood pressure level likewise may increase your risk.
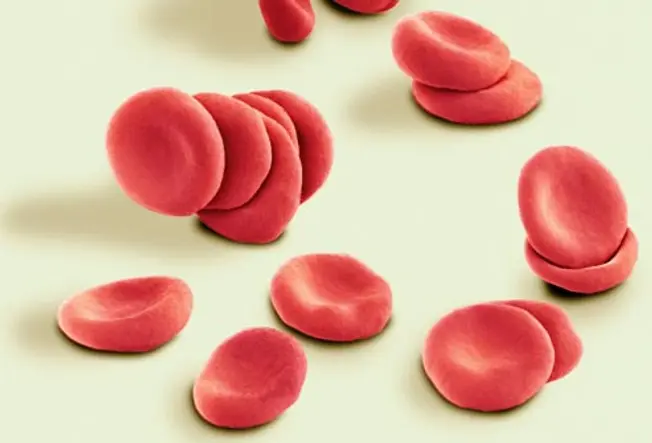
Complications: Fibroids and Anemia
viii/19
Some women with fibroids who experience unusually heavy bleeding during their periods may become anemic. Many cases of anemia due to iron deficiency from periods are mild and can be treated with a change in diet and iron supplement pills. Untreated anemia can lead to fatigue and languor -- and, in astringent cases, center issues.

Complications: Getting Meaning
9/19
Fibroids ordinarily practice non interfere with fertility and pregnancy. However, some women with fibroids experience more pregnancy complications and delivery risks. Fibroids may crusade the baby to exist in an abnormal position and tin cause preterm labor. They may likewise cause pelvic hurting and heavy bleeding later delivery, which may require surgery. In some instances, fibroids may cake your fallopian tubes. Fibroids growing along the inner uterine wall may brand information technology hard for a fertilized egg to attach.
When to Run across a Doctor
10/19
Encounter your health care provider if yous have the post-obit fibroid symptoms:
- Heavy menstrual bleeding
- Periods that became more than painful
- Frequent urination or disability to command the flow of urine
- A change in the length of your period over three to 6 cycles
- New persistent pain or heaviness in lower abdomen or pelvis
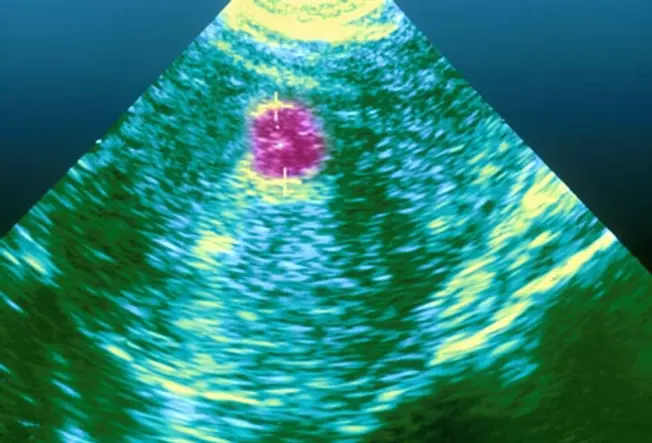
Diagnosis: Exam and Imaging
11/19
Your doctor may feel moderate and large uterine fibroids during a routine pelvic examination. Tests, such as an ultrasound, can show information about size and location of other fibroids. For women with fibroids who are trying to become significant, a test called a hysterosalpingogram volition evidence an outline of the uterus and fallopian tubes and may detect abnormalities. Other procedures to visualize the within of the uterus or abdomen as well may be needed.

Handling: Pain Medication
12/19
Pain medications, such as acetaminophen, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), like as ibuprofen or naproxen, can assist relieve menstrual cramping.
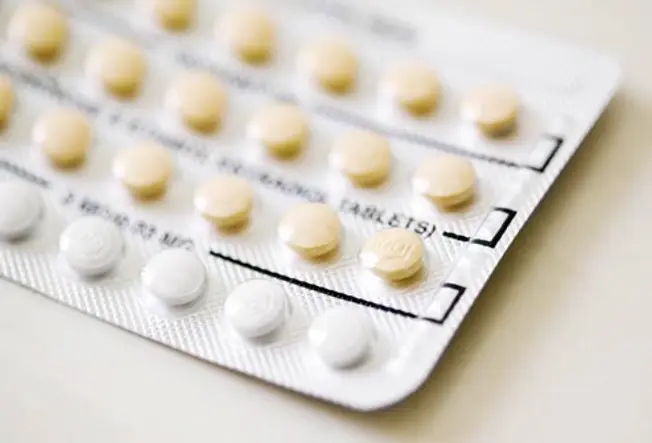
Treatment: Birth Command
13/19
Oral contraceptives manage levels of estrogen and progestin. This usually leads to lighter periods and tin alleviate some of the hurting associated with fibroids, such as heavy bleeding and cramping. Other hormonal birth command methods that may lessen coarse symptoms include progestin injections or progestin-releasing IUDs.
Other Hormone Therapies
14/19
Drugs called gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists may offer temporary symptom relief from fibroids by stopping periods and shrinking fibroids. GnRH agonists block the production of estrogen, so they can also cause bone loss, hot flashes, and vaginal dryness. Fibroids volition render to their previous size once handling ends. These may exist used to shrink fibroids earlier fibroid removal surgery.
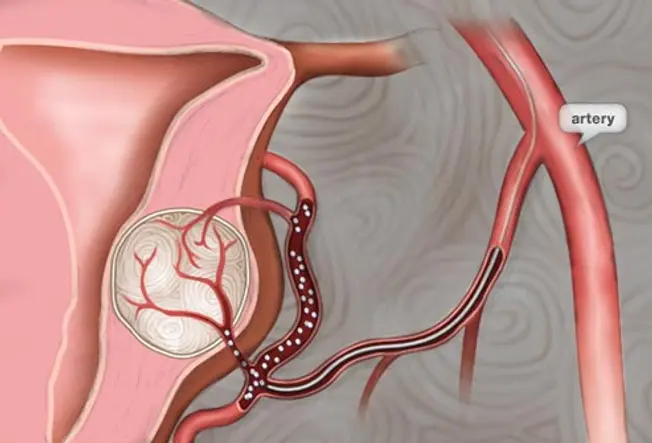
Handling: Embolization
15/19
For mild to moderate symptoms, uterine fibroid embolization may exist a good option. A catheter is guided to the uterine artery. Tiny particles of plastic or gelatin are then released into the claret vessels that feed the fibroid, causing it to compress over time. Embolization should not be an choice for women wanting to get pregnant at some point later treatment.
Handling: Surgery
xvi/19
A myomectomy typically removes the largest fibroids. It's is an option for women who want to still accept children. A hysterectomy is when the uterus is removed. There is a pocket-size chance that what was thought to be a fibroid could instead be a cancer called uterine sarcoma. For this reason, the FDA recommends not cut the fibroid into small-scale sections before removing information technology, a process called laparoscopic morcellation. Endometrial ablation, which is practiced for treating smaller fibroids, destroys the lining of the uterus, then pregnancy is non possible.
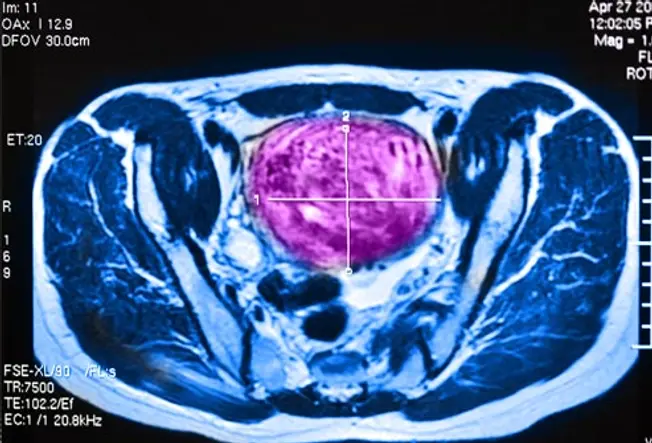
Treatment: Ultrasound
17/19
Ultrasound is one way to destroy fibroids without risk of damaging the uterus. The treatment uses high-intensity ultrasound waves that kill the fibroid tissue. Virtually women recover quickly from this procedure and can return to regular activities inside 24 hours. The long-term effects are still being studied, and information technology is not recommended for women who desire to become significant.

Fibroid Remedy: Exercise
18/19
Regular do may prevent fibroids. In one written report, women who exercised seven or more hours a week had significantly fewer fibroids than women who exercised less than two hours a calendar week. Obesity likewise is a risk factor for fibroids. And so exercising regularly tin can help you maintain a healthy weight and reduce your coarse adventure.

Care for Anemia
nineteen/xix
Women with fibroids who are not getting enough iron through nutrition solitary may develop anemia, where the body has fewer red claret cells than normal. Symptoms include fatigue, chest pain, and shortness of breath. Treatment may include eating more iron-rich foods, such as meats, poultry, fish, leafy greens, legumes, and atomic number 26-fortified breads and cereals. Your health care provider also may suggest fe supplements.
IMAGES PROVIDED BY: (1) Peggy Firth and Susan Gilbert for WebMD REFERENCES: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Show Sources
(two) CNRI / Photo Researchers
(3) Alix Minde/PhotoAlto
(four) Peggy Firth and Susan Gilbert for WebMD
(5) Dr. Barry Slaven/Visuals Unlimited
(vi) Peggy Firth and Susan Gilbert for WebMD
(seven) Priscilla Gragg/Blend Images
(8) Thomas Deerinck, NCMIR/SPL
(9) Lawren/Flickr
(10) Keith Brofsky/Photodisc
(xi) Dr. Pichard T/Photo Researchers
(12) Grove Pashley/Photographer's Choice
(xiii) Sarah M. Golonka/Brand Ten
(14) Nenov/Flickr
(15) Peggy Firth and Susan Gilbert for WebMD
(xvi) Dr. Najeeb Layyous/Photo Researchers
(17) Chru Tours-Garo, PHANIE/Photo Researchers
(18) Assembly/Photodisc
(nineteen) Kate Breakable/Flickr
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
American Pregnancy Association.
Baird, D. American Journal of Epidemiology, 2007.
Middle for Uterine Fibroids, Brigham and Women's Hospital.
Discovery Fit & Health.
Focused Ultrasound Surgery Foundation.
Gaskins, A.J. European Journal of Nutrition.
Merck Manual Home Wellness Handbook.
Myomectomy.net.
National Institute of Kid Wellness & Human Evolution.
National Uterine Fibroids Foundation.
New York Academy Langone Medical Center, department of obstetrics and gynecology.
Skilling, J. Fibroids: The Complete Guide to Taking Charge of Your Physical, Emotional, and Sexual Well-Beingness.
Guild of Interventional Radiology.
University of Maryland Medical Center.
University of N Carolina Coarse Care Clinic.
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
UptoDate: "Patient Data: Uterine Fibroids."
Uterine-Fibroids.org.
WomensHealth.gov: "Uterine fibroids fact sheet."
Yale School of Medicine, Obstetrics, Gynecology, & Reproductive Sciences.
FDA web site.
Source: https://www.webmd.com/women/uterine-fibroids/ss/slideshow-fibroid-overview
Posted by: sandersfrethe.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What Is The Tissue Makeup Of A Fibroid Tumor"
Post a Comment